2. Emphasis on prevention
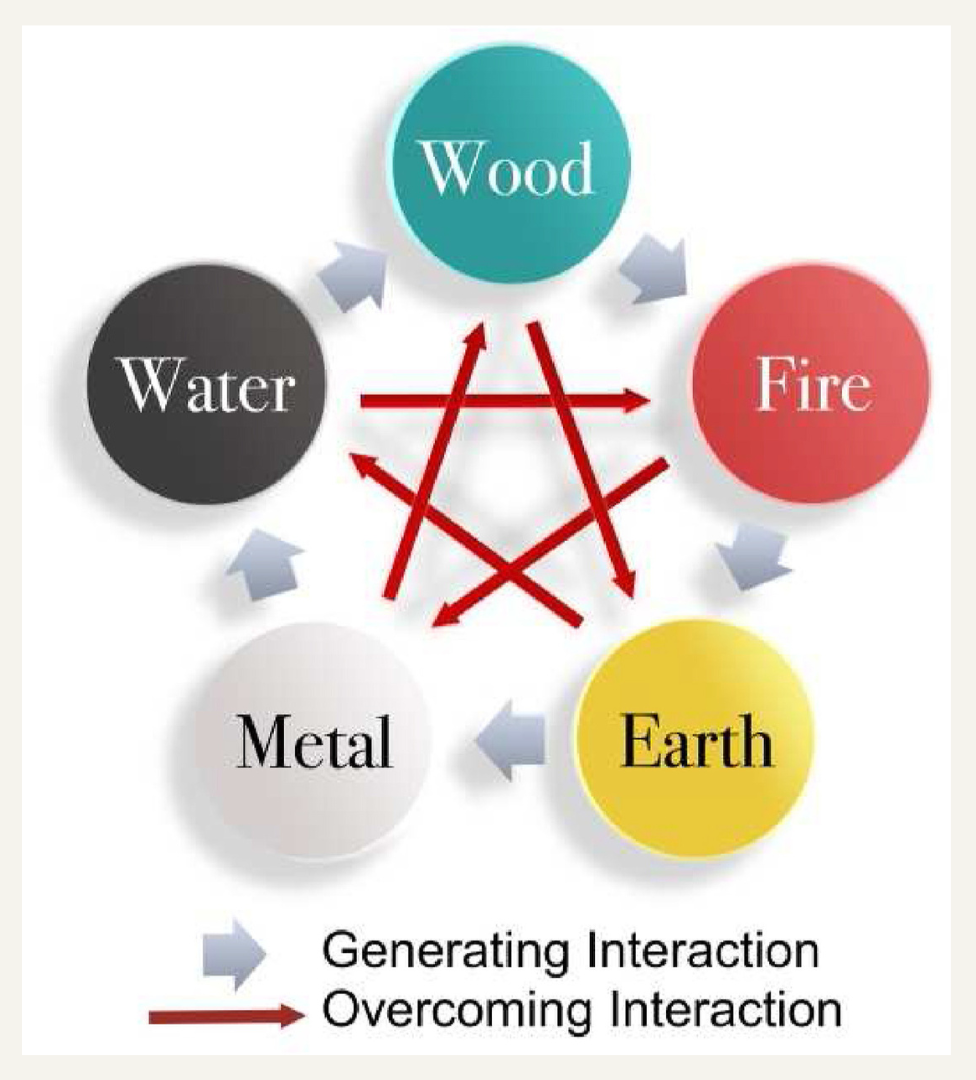
As human beings interact with everything in nature, it will be shown in an appearance referred to as “image”. The method of evaluating signs of the human body through external observation and internal speculation is called “image thinking”, a core characteristic of TCM. This method is further developed into a rich theory on the recognition of pathological signs at four layers of the human body, from the outermost weifen layer to the innermost xuefen layer.
Disease presentation and, thus, prevention usually follows this direction, going from external and obvious to the internal and obscure. The method is useful in detecting minor symptoms and prescribing treatment prior to the full presentation of disease. For example, hepatitis B virus markers is proven to align with this disease presentation theory, opening opportunities for early intervention, leading to better outcomes and lower overall healthcare costs.
3. Affordable for all
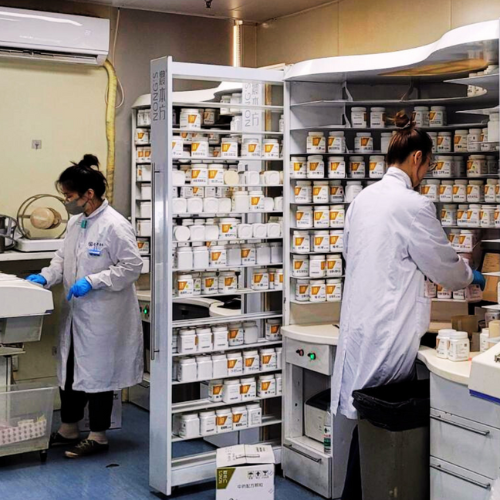
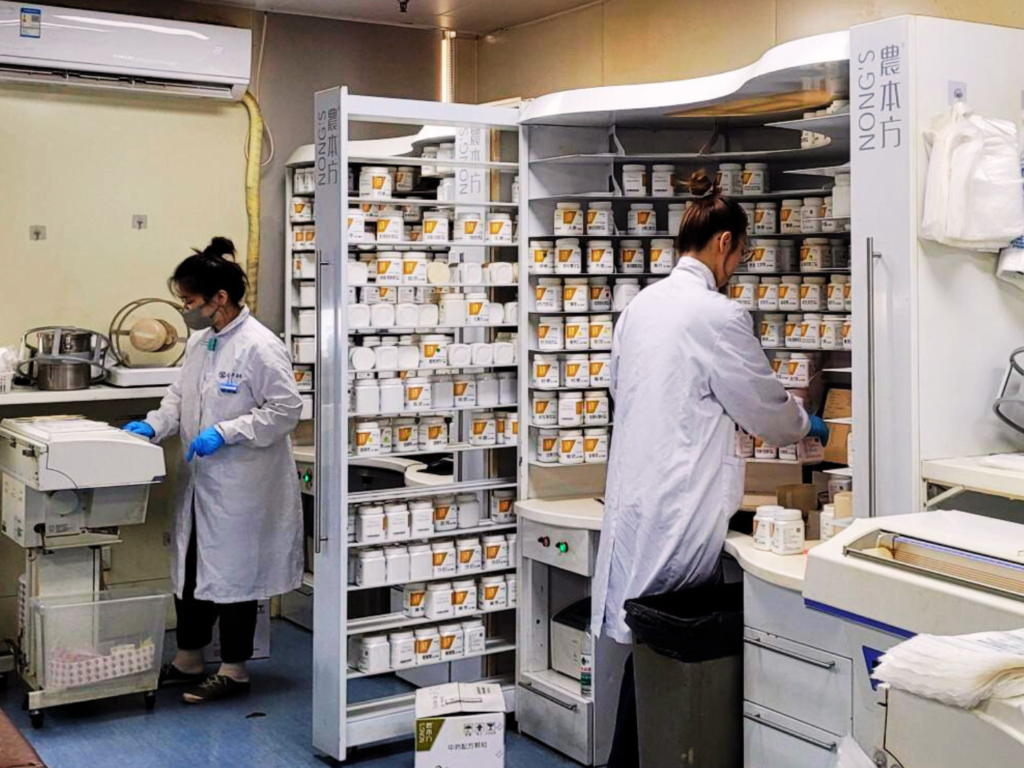
TCM medicine is primarily plant based and takes the form of herbal decoction made from medicinal plants, though ancient practitioners also included animal parts too. Volumes of publicly available pharmacopeia often act as definitive reference for medicine use where the properties of each medicinal plant with usage and preparation method carefully documented and further verified by modern studies.
TCM knowledge is built up by hundreds of years of practical knowledge and it belongs to all. This represents a fundamental difference in terms of pharmaceutical production where, unlike its Western counterparts, the absence of profit-minded gatekeepers among TCM pharmaceutical companies enable the cost of TCM drugs to remain affordable and accessible as production is streamlined and more efficient.
Holistic, preventative, and affordable are all key attributes of TCM that attest to its potential to contribute to universal healthcare. The key lies in the successful integration of TCM with Western medicine, incorporating a radically different viewpoint on human wellbeing in the healthcare system. As TCM matures in China, it has all the elements of scaling regionally to benefit a wider population. This ambition is rightly captured in China’s Health Silk Road, a set of health cooperation policies under the caveat of Belt and Road Initiative.
Ready to Scale
In 2023 alone, TCM pharmaceutical manufacturers recorded export volume reaching US$5.46 million to 196 markets, reaching as far as UK and Canada. TCM is also embracing digitalisation, adopting a more modern approach in its practices and delivery.
The advancement in artificial intelligence led to the creation of AI-powered tongue image diagnostics tools with over 80% accuracy. Deployed at scale, the diagnosis system can be installed at home to enable daily health monitoring. Coupled with telemedicine option, AI-optimised decoction preparation facility, and a mature network of distribution system, TCM can enable personalised health service in millions of households.
Efforts by ISO/TC 249 in standardising TCM medical nomenclatures, disease classification, and procedures are underway to prepare TCM for a greater international audience. As TCM continues to modernise and expand, it stands as a shining example of the potential of traditional and complementary medicine in contributing to global healthcare.
Now, imagine the same for the different forms of traditional medicine that are widely used throughout the region: India’s Ayurvedha, Thailand’s herbal medicine, Indonesia’s Jamu medicine, Japan’s eastern medicine, Malaysia and Brunei’s traditional Malay medicine etc.
How will the region’s healthcare system evolve if these medical systems are provided the platform and resources to modernise, develop, and integrate?
This critical question will be addressed in GIFT’s upcoming Asia Young Leaders Programme (AYLP). We will imagine the future of healthcare through the creation of a Regional Traditional and Complementary Medicine Hub that facilitates exchange not only on TCM but all Asian traditional medicines.
As the world grapples with rising healthcare costs, the exciting innovations such as this, will play a pivotal role in regional healthcare cooperation, advancing the mission of achieving universal health coverage for Asia and beyond. Now is the time to start prioritising this crucial dialogue.